What does cause white spots on the skin?
Publication date: 04-12-2023
Updated on: 13-12-2023
Topic: Dermatology
Estimated reading time: 1 min
Article Author
Elena Buonanno
Medical Editor
Antonino Di Pietro
Editor and Translator
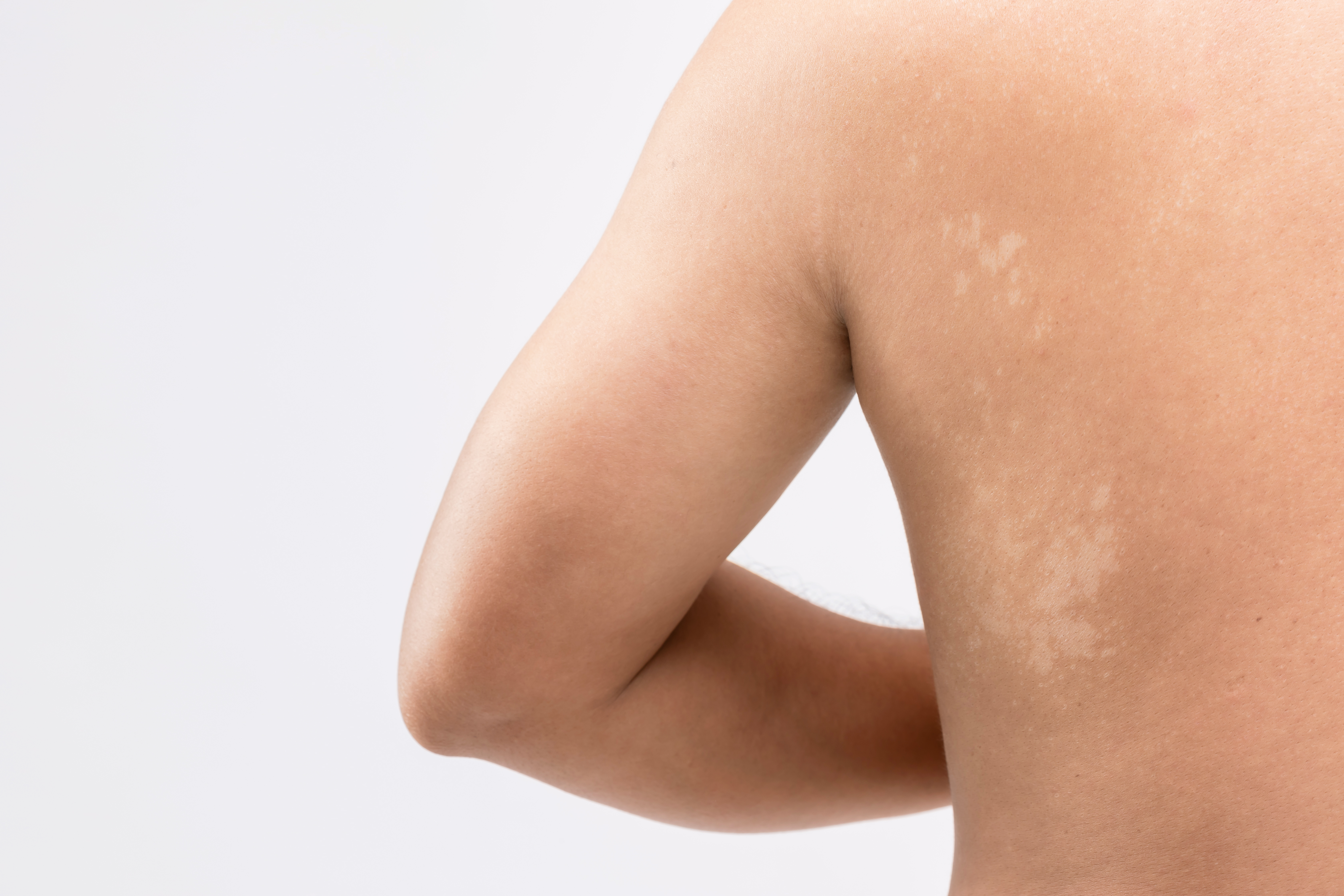
Viktoryia LuhakovaUpon returning from vacation, it can happen that you end up with white spots on your skin that ruin your tan. Don't be afraid. In most cases, this is not a dangerous phenomenon, but it is essential to see a dermatology specialist to identify the cause.
"White spots on the skin are related to a lack of melanin, a pigment that the skin produces in response to sun exposure to defend itself, which can depend on a variety of factors, from hereditary to the presence of a fungus. Therefore, in order to choose the most suitable treatment to solve the problem, it is essential to identify its origin," explains Professor Antonino Di Pietro, Scientific Director of the Vita Cutis Dermoclinical Institute at Palazzo della Salute Wellness Clinic.
Let us then delve with our expert into what white spots may be due to and how to get rid of them.
Why white spots appear on the skin?
White spots on the face, legs or other parts of the body can have several causes. Among these, the most common are:
- autoimmune skin diseases such as vitiligo;
- fungal infections as in the case of pityriasis;
- idiopathic (i.e., without specific cause) skin pigmentation disorders such as for guttate hypomelanosis.
Aging can also promote the appearance of the problem, as the cells that produce melanin (melanocytes) shrink with age. Let us see in more detail what these disorders and pathologies consist of.
Vitiligo
"Vitiligo, which can affect any skin type and phototype, is a skin blemish determined by a loss of melanocytes in certain areas of the face and body. The consequence is the formation of lighter spots on the skin.
The causes of vitiligo are still unclear:
- in some cases, it may occur in people who already have other autoimmune diseases;
- in other cases, however, it can appear as a result of severe stress;
- it can also be transmitted hereditarily," Professor Di Pietro notes.
Pityriasis
The term pityriasis, however, refers to 2 types of skin manifestations:
- pityriasis versicolor: it is a skin infection due to a fungus, Pityrosporum orbicularis or Malassezia furfur, which usually lives on the skin without causing problems, but can become aggressive under certain circumstances. Fungal growth alters normal skin pigmentation by promoting the appearance of small white spots, usually on the upper body (trunk, back, and neck). Commonly referred to as “sea fungus,” it does not actually promote infection, simply the spots become evident after the summer when you start to lose your tan;
- pityriasis alba: it is an eczema that occurs mainly in childhood and, under the effect of sunlight, undergoes some changes leading to the appearance of white patches with a characteristic oval or roundish shape, with ill-defined margins and a desquamated part in the center.
Hypomelanosis guttata
Finally, among the causes, there may also be what is known as guttate hypomelanosis, a skin blemish that mainly affects women over 40 and is concentrated in body parts such as legs and forearms, which usually correspond to the body areas most exposed to the sun.
"Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, also called lenticular leukoderma, is a blemish resulting from melanocyte damage that manifests as white patches with sharp margins about 5 mm in size. These spots are visible in summer after sun exposure, and partly caused by improper sun exposure, and fade as the skin returns to its natural complexion.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis is a relapsing disorder: if no action is taken, it will recur at the first opportunity of sun exposure for prolonged times."
How to prevent white spots?
The first and fundamental rule to prevent the formation of white dots and spots on the skin is to properly protect yourself from the sun with a sunscreen with a high SPF.
Targeted treatments according to the cause to eliminate them
The choice of treatments to eliminate white spots depends on the cause: "Regarding vitiligo, topical cortisone treatments may be useful in some cases. In other cases, photosensitizing drugs can be combined with controlled sun exposure, so as to try to “awaken” melanocyte activities. There are also therapies with vitamin D, a substance that mimics the effects of the sun.
Phototherapy, whereby depigmented areas are exposed to UVB rays, is also effective. At least 5 sessions are recommended, and the results you get can be very satisfactory, although they do not completely eliminate the white patches of vitiligo.
If, on the other hand, the spots are dependent on the presence of a fungus, treatment consists mainly of medically indicated antifungal treatments and medications to be applied to the skin (creams, sprays, or lotions).
For whiteheads due to guttate hypomelanosis, in addition to applying high protection before sun exposure so as to prevent their reappearance, it is very helpful to keep the skin properly moisturized by choosing a moisturizer with phospholipids and glucosamine. Treatment at the dermatologist with lasers can then be used to eliminate them.
Obviously, in all cases it will be the specialist who will indicate the most suitable therapy depending on the problem, the extent and also the characteristics of the patient's skin," Professor Di Pietro concludes.